In this example we connect an Ethernet shield to an Arduino, we then connect a MPL3115A2 sensor to this and we will display the readings on a webpage
Lets take a look at the MPL3115A2.
The MPL3115A2 is a compact, piezoresistive, absolute pressure sensor with an I2C digital interface. MPL3115A2 has a wide operating range of 20 kPa to 110 kPa, a range that covers all surface elevations on earth. The MEMS is temperature compensated utilizing an on-chip temperature sensor. The pressure and temperature data is fed into a high resolution ADC to provide fully compensated and digitized outputs for pressure in Pascals and temperature in °C.
The compensated pressure output can then be converted to altitude, utilizing the formula stated in Section 9.1.3 “Pressure/altitude” provided in meters.The internal processing in MPL3115A2 removes compensation and unit conversion load from the system MCU, simplifying system design
Parts List
| Part | Link |
| Arduino Uno | UNO R3 CH340G/ATmega328P, compatible for Arduino UNO |
| MPL3115A2 module | MPL3115A2 I2C Intelligent Temperature Pressure Altitude Sensor V2.0 for Arduino |
| Connecting cable | Free shipping Dupont line 120pcs 20cm male to male + male to female and female to female jumper wire |
| Arduino Ethernet shield | Ethernet Shield W5100 R3 UNO and Mega 2560 |
Schematics/Layout
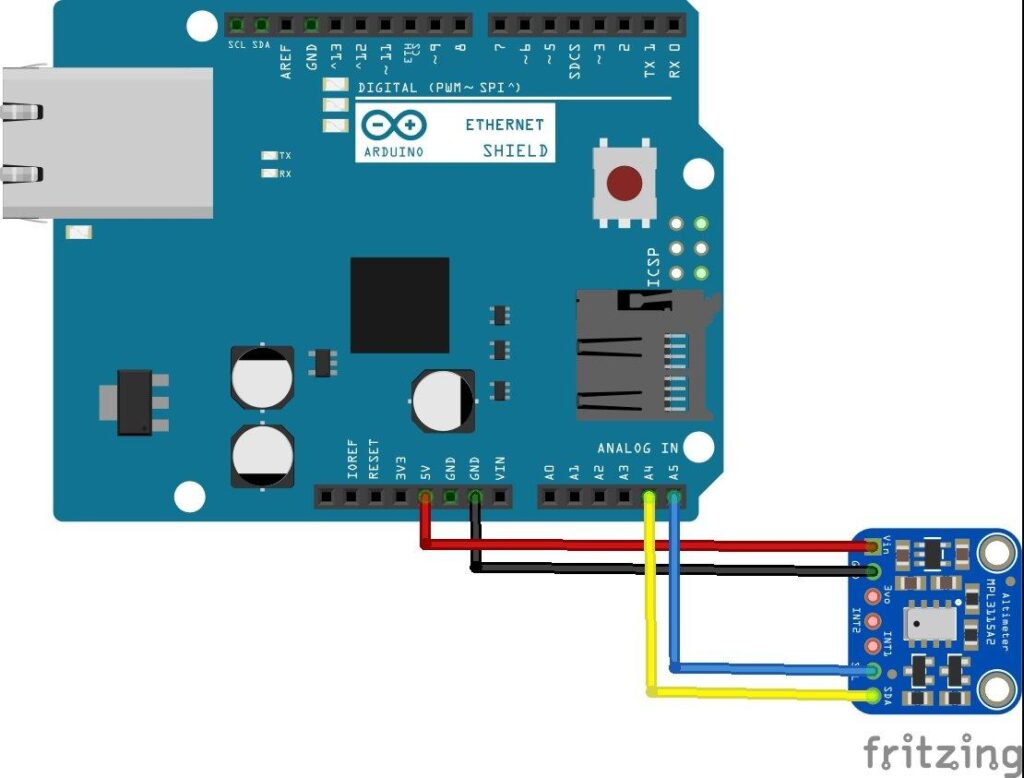
Connect the Ethernet shield and the connect the sensor to the shield connector, like this.
Code
Again we use a library for the sensor, the rest are built in libraries – https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_MPL3115A2_Library
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_MPL3115A2.h>
Adafruit_MPL3115A2 baro = Adafruit_MPL3115A2();
// Enter a MAC address and IP address for your controller below.
// The IP address will be dependent on your local network:
byte mac[] = {
0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED };
IPAddress ip(192,168,1, 177);
// Initialize the Ethernet server library
EthernetServer server(80);
void setup()
{
// Open serial communications
Serial.begin(9600);
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
server.begin();
Serial.print("server is at ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
}
void loop()
{
if (! baro.begin())
{
Serial.println("Couldnt find sensor");
return;
}
// listen for incoming clients
EthernetClient client = server.available();
if (client)
{
Serial.println("new client");
boolean currentLineIsBlank = true;
while (client.connected())
{
if (client.available())
{
char c = client.read();
Serial.write(c);
if (c == '\n' && currentLineIsBlank)
{
// send a standard http response header
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println("Connnection: close");
client.println();
client.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML>");
client.println("<html>");
client.println("<meta http-equiv=\"refresh\" content=\"5\">");
client.println("<br />");
float pascals = baro.getPressure();
client.print("pressure (Inches (Hg)): ");
client.println((float)pascals/3377, 1);
client.println("<br />");
client.print("Temperature (C): ");
client.println((float)baro.getTemperature(), 1);
client.println("<br />");
client.print("Altitude (m): ");
client.println((float)baro.getAltitude(), 1);
client.println("<br />");
client.println("</html>");
break;
}
if (c == '\n')
{
currentLineIsBlank = true;
}
else if (c != '\r')
{
currentLineIsBlank = false;
}
}
}
// give the web browser time to receive the data
delay(1);
// close the connection:
client.stop();
Serial.println("client disonnected");
}
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open your favourite web browser and type in the IP address, you should see something like this
pressure (Inches (Hg)): 29.7
Temperature (C): 19.1
Altitude (m): 84.1
Links
https://www.nxp.com/docs/en/data-sheet/MPL3115A2.pdf